
Biomarkers are crucial in healthcare as they act as measurable indicators of a person’s health status, allowing for early detection of diseases, monitoring disease progression, predicting treatment response, and identifying individuals at high risk for specific conditions, essentially enabling personalized medicine by providing insights into the underlying biological processes at play within
an individual.
Key Uses for Medical Biomarkers:
Early Disease Detection:
Biomarkers can signal the presence of a disease even before symptoms appear, enabling early intervention and potentially improved treatment outcomes.
Disease Monitoring:
By tracking biomarker levels over time, healthcare professionals can monitor disease progression and assess the effectiveness of treatment interventions.
Risk Assessment:
Certain biomarkers can identify individuals at higher risk for developing specific diseases, allowing for preventive measures to
be taken.
Personalized Medicine:
Biomarkers can help tailor treatment plans to individual patients based on their unique biological characteristics, leading to more targeted therapies.
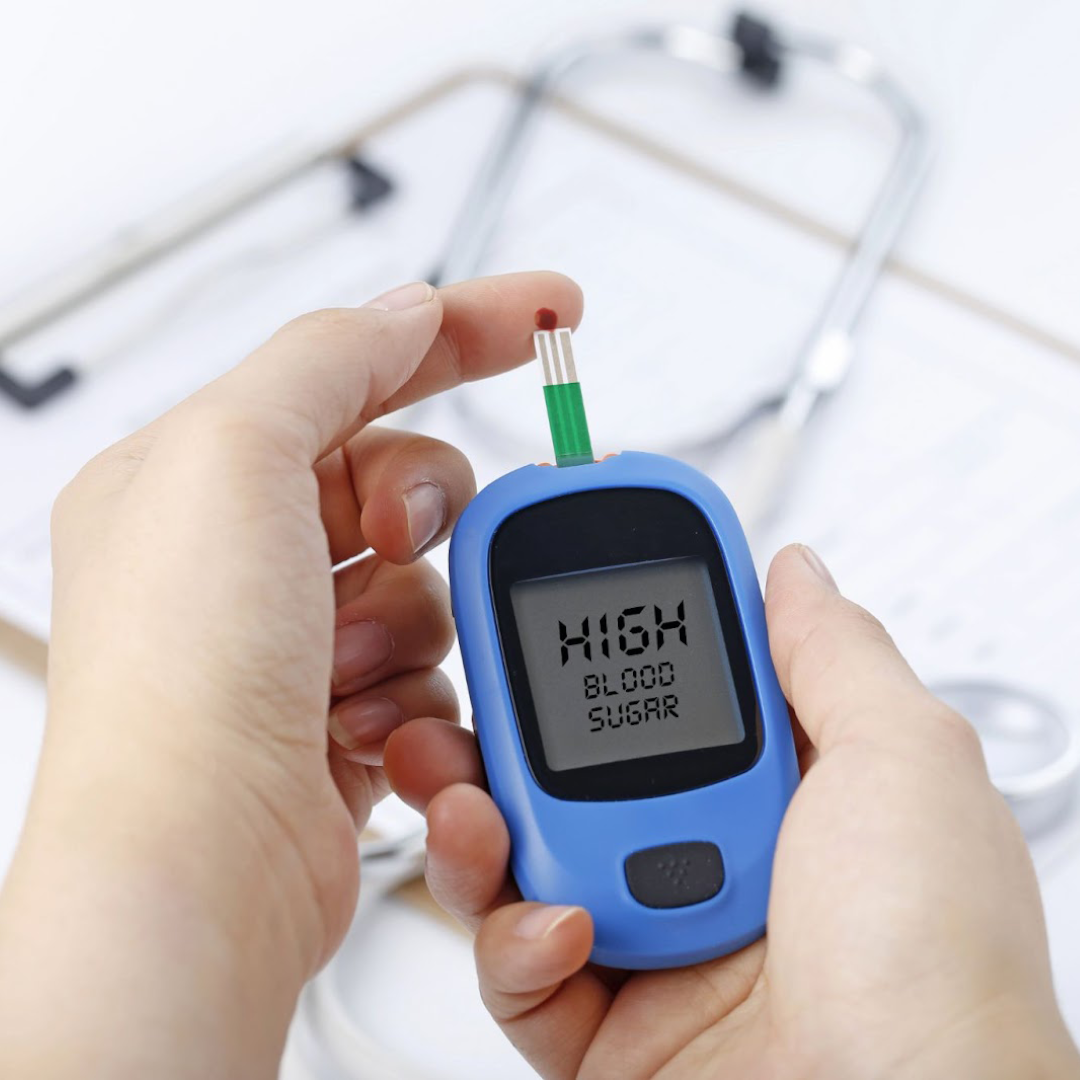
A metabolic disorder caused by excess blood glucose levels, is a key example of disease caused by homeostatic imbalance. In ideal circumstances, homeostatic control mechanisms should prevent this imbalance from occurring. However, in some people, the mechanisms do not work efficiently enough or the amount of blood glucose is too great to be effectively managed. In these cases, medical intervention is necessary to restore homeostasis and prevent permanent organ damage.

Failed homeostasis can lead to atherosclerosis. This is a chronic inflammatory response in the walls of arteries that causes plaque to build up. Plaque can restrict blood flow, which can lead to heart disease.
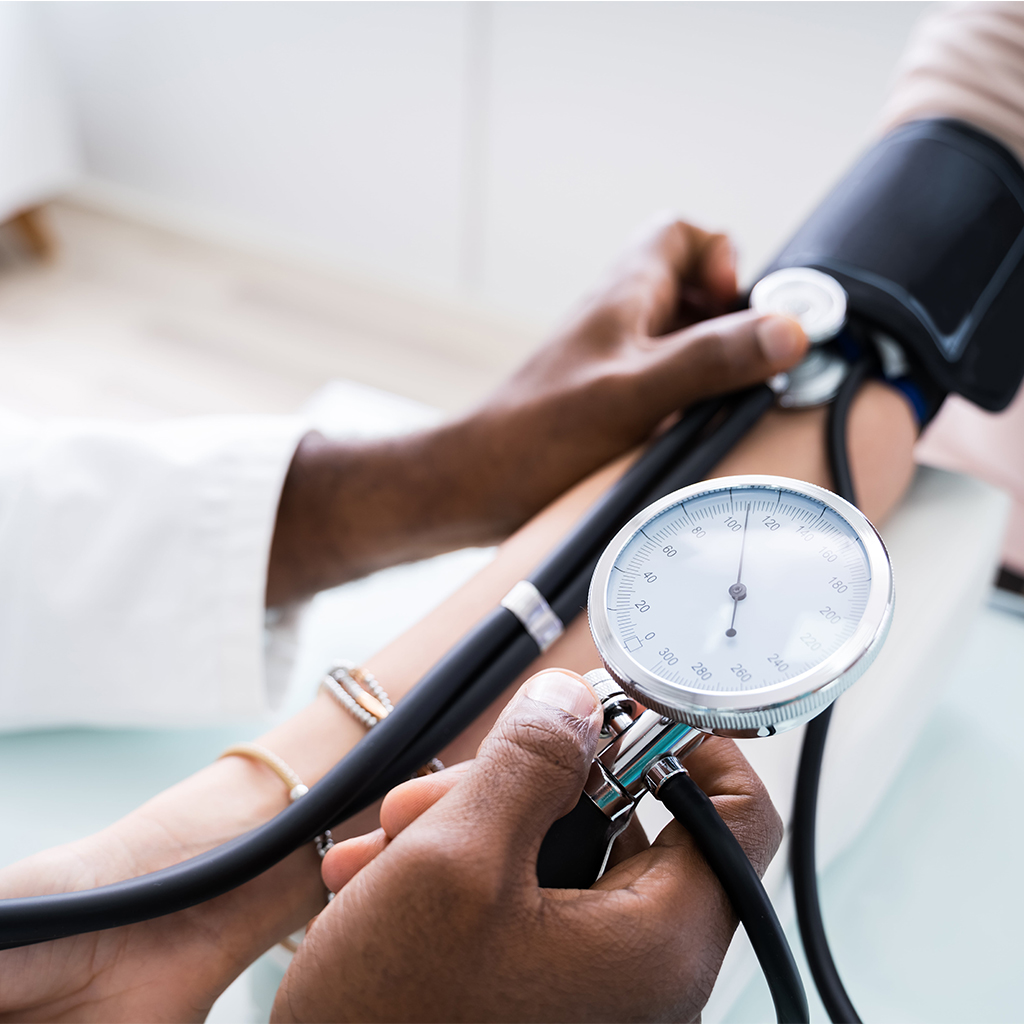
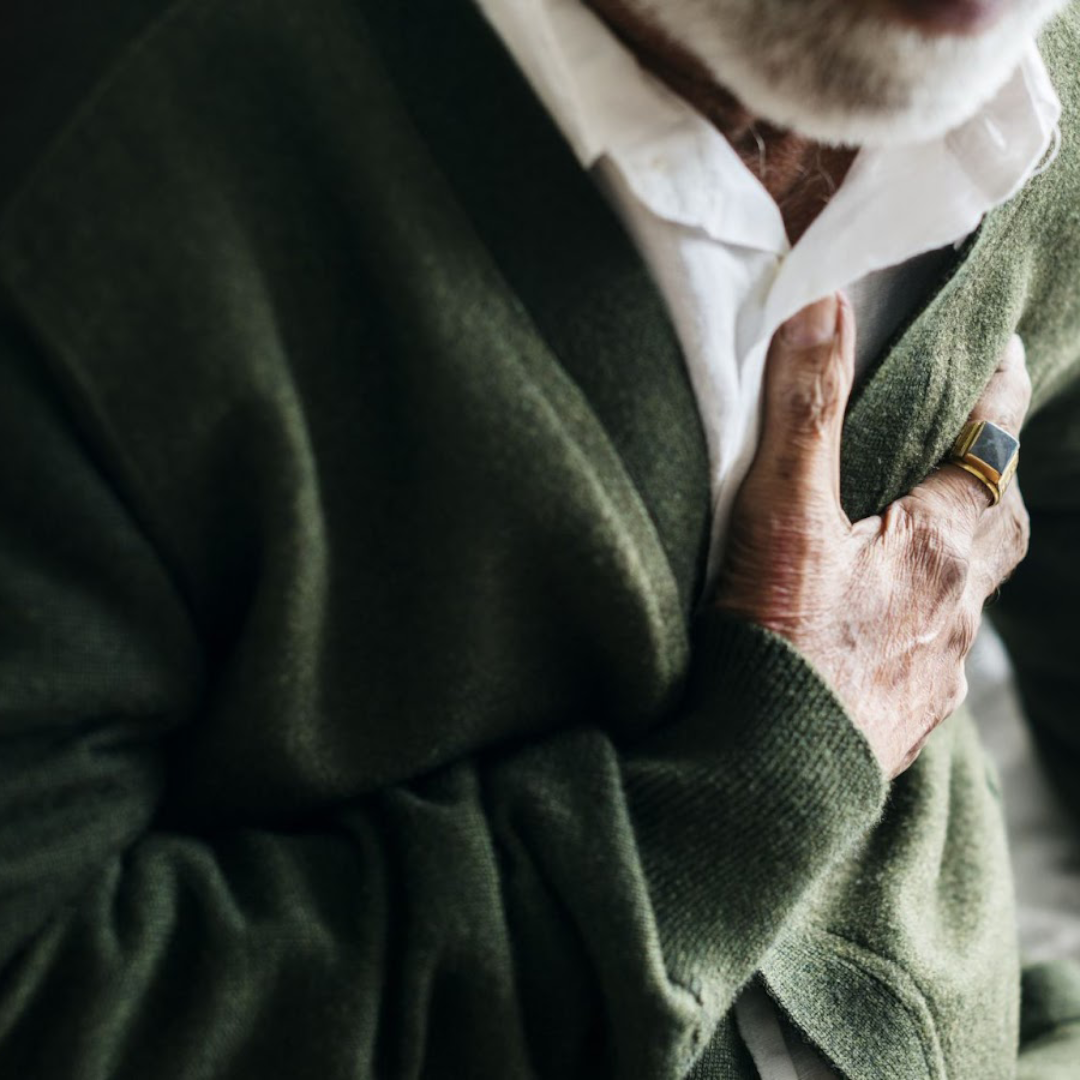
Another disorder that can result from homeostatic imbalance. This condition occurs when the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is too high. Over time, this can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease and stroke.